
How Innovation Is Reshaping Recovery, Mobility, and Cost Containment
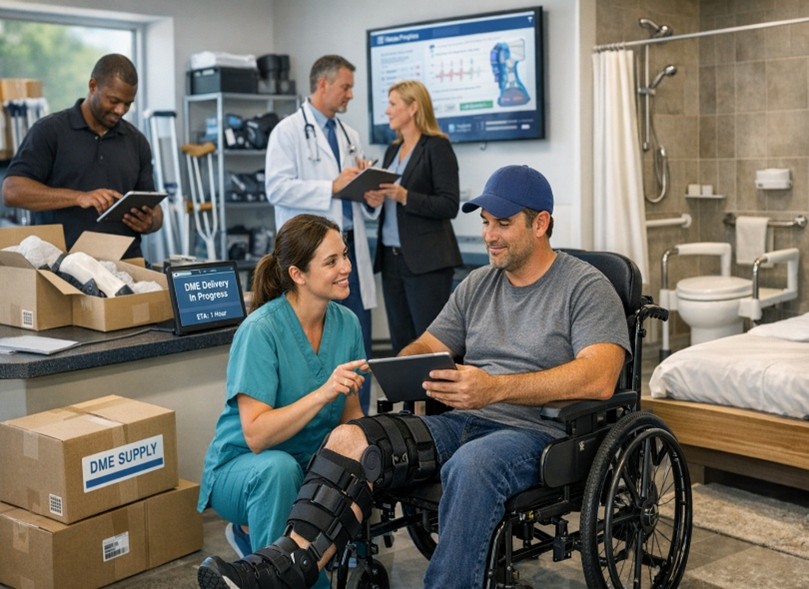 Durable Medical
Equipment (DME) has long played a crucial role in workers’ compensation
programs, supporting injured employees with the tools they need to recover
safely and regain independence. From orthopedic braces and wheelchairs to home
safety modifications, DME allows individuals to transition from hospital care
to functional daily living. Historically, however, this segment of claims
management has been slowed by outdated procurement models, limited
customization, and inconsistent oversight. Today, a wave of innovation — driven
by technology, clinical collaboration, and evolving patient needs — is
transforming how DME is prescribed, delivered, and managed in the workers’
compensation system. At its core, DME is designed to enhance mobility, promote
healing, and reduce the risk of reinjury. Yet traditional distribution
pipelines often created barriers: long waits for equipment delivery, lack of
patient education, and difficulty ensuring the right device reached the right
worker at the right time. These delays could stall recovery, contribute to
unnecessary medical utilization, or extend time away from work. As the industry
places increasing emphasis on early intervention and continuity of care,
improving DME access and quality has become a primary focus for payers, case
managers, and providers alike.
Durable Medical
Equipment (DME) has long played a crucial role in workers’ compensation
programs, supporting injured employees with the tools they need to recover
safely and regain independence. From orthopedic braces and wheelchairs to home
safety modifications, DME allows individuals to transition from hospital care
to functional daily living. Historically, however, this segment of claims
management has been slowed by outdated procurement models, limited
customization, and inconsistent oversight. Today, a wave of innovation — driven
by technology, clinical collaboration, and evolving patient needs — is
transforming how DME is prescribed, delivered, and managed in the workers’
compensation system. At its core, DME is designed to enhance mobility, promote
healing, and reduce the risk of reinjury. Yet traditional distribution
pipelines often created barriers: long waits for equipment delivery, lack of
patient education, and difficulty ensuring the right device reached the right
worker at the right time. These delays could stall recovery, contribute to
unnecessary medical utilization, or extend time away from work. As the industry
places increasing emphasis on early intervention and continuity of care,
improving DME access and quality has become a primary focus for payers, case
managers, and providers alike.
One of the most notable advancements is the integration of technology into both equipment design and distribution. Modern DME suppliers are increasingly adopting digital platforms that streamline ordering and automate tracking, allowing case managers to monitor authorization status, shipment progress, and maintenance needs in real time. This level of transparency reduces administrative friction and shortens turnaround times, enabling injured workers to put equipment to use without unnecessary delay. Some vendors now offer centralized portals where clinicians, adjusters, and case managers collaborate within a single system, simplifying communication and reducing the likelihood of misalignment.
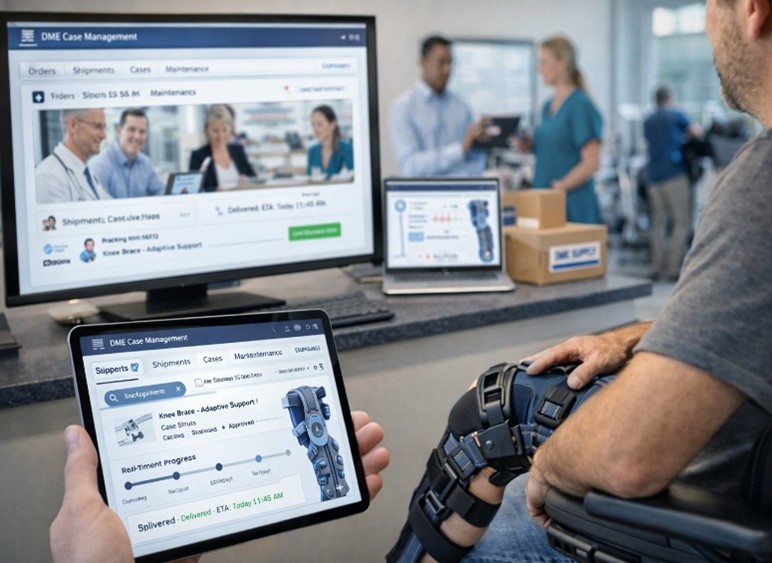 In addition to
improved logistics, DME itself has evolved. Equipment that once followed a
one-size-fits-all model is becoming more personalized, lightweight, and
adaptable. Orthopedic bracing systems now offer dynamic support that responds
to movement rather than rigid immobilization, allowing employees to maintain
function while promoting healing. Advances in materials science have introduced
stronger, yet lighter, components that improve comfort and increase patient
compliance. These changes are not merely cosmetic — better-designed devices
translate directly into faster recovery trajectories and fewer complications.
Workers who feel comfortable using prescribed equipment are more likely to
follow recommended treatment pathways, reducing the risk of reinjury and
avoiding costly downstream care.
In addition to
improved logistics, DME itself has evolved. Equipment that once followed a
one-size-fits-all model is becoming more personalized, lightweight, and
adaptable. Orthopedic bracing systems now offer dynamic support that responds
to movement rather than rigid immobilization, allowing employees to maintain
function while promoting healing. Advances in materials science have introduced
stronger, yet lighter, components that improve comfort and increase patient
compliance. These changes are not merely cosmetic — better-designed devices
translate directly into faster recovery trajectories and fewer complications.
Workers who feel comfortable using prescribed equipment are more likely to
follow recommended treatment pathways, reducing the risk of reinjury and
avoiding costly downstream care.
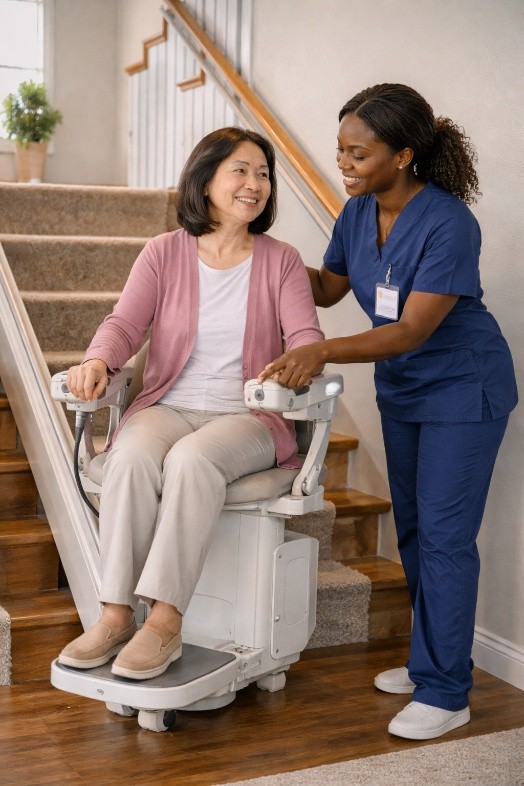 Another significant
development is the shift toward patient-centered DME education and support, an
area historically overlooked in claims management. Simply delivering a device
does not guarantee effective use. Today’s leading suppliers pair equipment with
instructional resources, virtual coaching, and multilingual guidance to ensure
workers understand proper fitting, maintenance, and safety. This is especially
valuable in workers’ compensation, where recovery takes place outside the
traditional healthcare setting. When injured employees know how to use their
equipment confidently, barriers fall and independence grows. Home modification
services and assistive technologies have followed a similar upward trend,
expanding well beyond grab bars and basic ramps. Modular stair lifts, ergonomic
workstation equipment, improved transfer devices, and customized bathroom
safety solutions now allow workers with significant injuries to remain at home
rather than move into long-term care settings. This type of innovation not only
enhances quality of life, but also contains cost by reducing facility stays,
caregiver needs, and secondary medical complications. The ability to keep
workers safely in their homes aligns perfectly with the primary goals of
workers’ compensation: recovery, dignity, and return to productive function.
Another significant
development is the shift toward patient-centered DME education and support, an
area historically overlooked in claims management. Simply delivering a device
does not guarantee effective use. Today’s leading suppliers pair equipment with
instructional resources, virtual coaching, and multilingual guidance to ensure
workers understand proper fitting, maintenance, and safety. This is especially
valuable in workers’ compensation, where recovery takes place outside the
traditional healthcare setting. When injured employees know how to use their
equipment confidently, barriers fall and independence grows. Home modification
services and assistive technologies have followed a similar upward trend,
expanding well beyond grab bars and basic ramps. Modular stair lifts, ergonomic
workstation equipment, improved transfer devices, and customized bathroom
safety solutions now allow workers with significant injuries to remain at home
rather than move into long-term care settings. This type of innovation not only
enhances quality of life, but also contains cost by reducing facility stays,
caregiver needs, and secondary medical complications. The ability to keep
workers safely in their homes aligns perfectly with the primary goals of
workers’ compensation: recovery, dignity, and return to productive function.
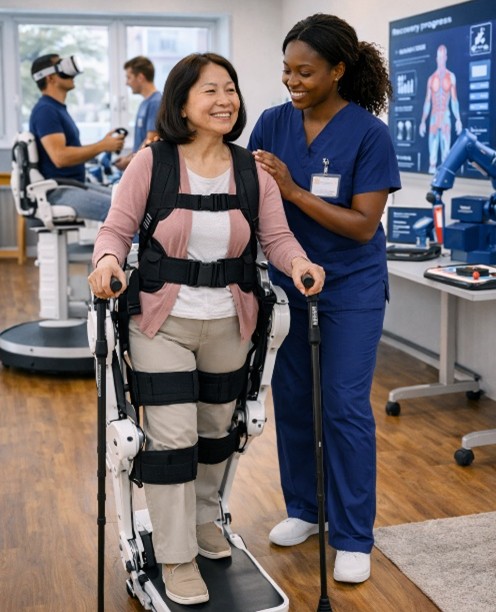 Looking ahead, the
DME landscape within workers’ compensation will continue to evolve, driven by
both workforce demographics and technology innovation. As aging employees
remain in physically demanding roles and injury severities shift with workplace
trends, demand for supportive equipment will expand. Virtual reality therapy
tools, robotic assistive devices, and adaptive exoskeleton technologies — once
only seen in research environments — are beginning to appear in real-world
occupational injury recovery discussions. Whether these tools become mainstream
or remain specialty resources, their emergence underscores a broader trend:
technology-enabled equipment will increasingly supplement traditional physical
therapy and assistive care. Advancing durable medical equipment is not only
about access to new products; it is about improving the entire experience of
healing. Faster distribution, smarter tracking, patient-centered support, and
clinical collaboration all contribute to better outcomes — and a workers’ compensation
system that delivers on its promise to protect and restore the individuals who
power our workforce every day.
Looking ahead, the
DME landscape within workers’ compensation will continue to evolve, driven by
both workforce demographics and technology innovation. As aging employees
remain in physically demanding roles and injury severities shift with workplace
trends, demand for supportive equipment will expand. Virtual reality therapy
tools, robotic assistive devices, and adaptive exoskeleton technologies — once
only seen in research environments — are beginning to appear in real-world
occupational injury recovery discussions. Whether these tools become mainstream
or remain specialty resources, their emergence underscores a broader trend:
technology-enabled equipment will increasingly supplement traditional physical
therapy and assistive care. Advancing durable medical equipment is not only
about access to new products; it is about improving the entire experience of
healing. Faster distribution, smarter tracking, patient-centered support, and
clinical collaboration all contribute to better outcomes — and a workers’ compensation
system that delivers on its promise to protect and restore the individuals who
power our workforce every day.
Workers’ compensation provides financial and medical benefits to employees who suffer work-related injuries or illnesses. However, ensuring the appropriate use of medical services is crucial for cost control and effective recovery. Utilization review (UR) serves as a safeguard to evaluate the necessity, efficiency, and appropriateness of medical treatments, ensuring injured workers receive the best possible care without unnecessary procedures or excessive costs.
 What Is Utilization Review?
What Is Utilization Review?
Utilization review assesses medical treatment requests to determine whether they align with industry guidelines, evidence-based practices, and regulatory requirements. This process ensures injured employees receive necessary care while preventing excessive treatments that could drive up workers’ compensation costs.
UR typically involves three types of reviews:
Key Benefits of Utilization Review
Ensures Appropriate Medical Treatment
 UR confirms that medical treatments align with industry-recognized standards and guidelines, such as the Official Disability Guidelines (ODG). This prevents overuse of medical procedures that may not be necessary, ensuring patients receive care tailored to their condition without excessive treatments.
UR confirms that medical treatments align with industry-recognized standards and guidelines, such as the Official Disability Guidelines (ODG). This prevents overuse of medical procedures that may not be necessary, ensuring patients receive care tailored to their condition without excessive treatments.
By verifying treatment requests, utilization review minimizes the risk of prolonged medical interventions that may hinder recovery instead of aiding it.
Controls Costs and Prevents Overutilization
Workers’ compensation medical expenses can escalate due to unnecessary treatments, repeat procedures, or prolonged therapies. UR helps mitigate these costs by ensuring only effective and medically necessary treatments are approved.
For example, if a doctor requests extended physical therapy beyond recognized treatment protocols, utilization review may recommend an appropriate duration, preventing excessive expenses while maintaining effective rehabilitation.
Promotes Faster Recovery and Return to Work
 Utilization review ensures injured workers receive timely and appropriate medical care, reducing delays in treatment approvals. When treatments align with recognized protocols, employees can recover efficiently and return to work sooner.
Utilization review ensures injured workers receive timely and appropriate medical care, reducing delays in treatment approvals. When treatments align with recognized protocols, employees can recover efficiently and return to work sooner.
This process also helps case managers and employers develop return-to-work plans that accommodate medical restrictions while promoting active recovery.
Reduces Fraud and Abuse
Workers’ compensation fraud occurs when medical providers bill for unnecessary treatments or services that were not performed. UR acts as a safeguard against fraudulent billing practices by verifying the necessity of requested treatments.
By assessing medical requests objectively, insurers and employers can prevent fraudulent claims and ensure resources are used appropriately.
Improves Compliance with Regulations
Workers’ compensation laws vary by state, and medical treatments must adhere to specific regulations. Utilization review ensures medical care meets compliance requirements, reducing disputes, legal risks, and administrative burdens.
Employers and insurers benefit from UR by maintaining regulatory transparency, reducing claim disputes, and streamlining approval processes.
Enhances Communication and Collaboration
The utilization review process fosters better communication among healthcare providers, insurers, and case managers. Physicians submit treatment requests, while review teams assess their necessity, ensuring all stakeholders remain informed about medical decisions.
This structured communication supports efficient medical planning, helping injured employees receive appropriate treatment while minimizing unnecessary costs.
 Utilization review is a vital component of the workers’ compensation system, ensuring injured employees receive medically necessary treatments while controlling costs, preventing fraud, and promoting faster recovery. By reviewing treatment requests and aligning them with evidence-based guidelines, UR enhances the efficiency and fairness of medical care in workers’ compensation.
Utilization review is a vital component of the workers’ compensation system, ensuring injured employees receive medically necessary treatments while controlling costs, preventing fraud, and promoting faster recovery. By reviewing treatment requests and aligning them with evidence-based guidelines, UR enhances the efficiency and fairness of medical care in workers’ compensation.
For employers, insurers, and healthcare providers, effective utilization review processes balance cost management with high-quality patient care, helping injured workers recover promptly and return to work safely.
 When managing complex medical cases, employers, insurers, and healthcare professionals often rely on case managers to coordinate care, streamline recovery, and optimize patient outcomes. Case management can be conducted in two primary ways: field case management and telephonic case management. While both approaches aim to support injured workers or patients through their recovery process, each has unique advantages depending on the situation.
When managing complex medical cases, employers, insurers, and healthcare professionals often rely on case managers to coordinate care, streamline recovery, and optimize patient outcomes. Case management can be conducted in two primary ways: field case management and telephonic case management. While both approaches aim to support injured workers or patients through their recovery process, each has unique advantages depending on the situation.
What Is Field Case Management?
Field case management, on the other hand, involves face-to-face interactions between the case manager and the patient, healthcare providers, and sometimes the employer. Field case managers visit patients at their homes, workplaces, or healthcare facilities to provide hands-on assessments and more personalized support.
Benefits of Field Case Management
 Direct support improves compliance with medical treatments and rehabilitation plans.
Direct support improves compliance with medical treatments and rehabilitation plans. What Is Telephonic Case Management?
What Is Telephonic Case Management?
Telephonic case management involves managing cases remotely via phone calls, emails, or video conferencing. It is a convenient and cost-effective method that allows case managers to assess and assist patients without direct physical interaction. Telephonic case managers coordinate care by gathering medical updates, scheduling treatments, monitoring progress, and providing guidance—all through remote communication.
Benefits of Telephonic Case Management
When to Choose Field Case Management Over Telephonic Case Management
While telephonic case management is effective for routine follow-ups and straightforward cases, field case management is invaluable for:
Severe or Complex Injuries: Patients requiring extensive medical intervention or specialized care benefit from in-person assessments.
 Behavioral Health Cases: Patients dealing with psychological or emotional conditions may require direct engagement for better support.
Behavioral Health Cases: Patients dealing with psychological or emotional conditions may require direct engagement for better support.
Return-to-Work Evaluations: Field case managers can visit workplaces to assess modifications needed for a safe and effective return.
Workers’ Compensation Cases with Delays: In cases where recovery is stagnating or disputes arise, a field case manager’s intervention can expedite resolution.
Both field case management and telephonic case management have important roles in supporting patient recovery and case coordination. Telephonic case management excels in cost efficiency and accessibility, making it a great choice for straightforward cases. However, field case management provides deeper engagement, personalized care, and stronger collaboration—leading to better overall outcomes.
 In today’s fast-paced world, many of us spend hours working at desks, lifting heavy objects, or engaging in repetitive tasks. Without proper ergonomic practices, these activities can lead to discomfort, pain, and even long-term injuries. Fortunately, by incorporating ergonomics into our daily routine, we can significantly reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and improve overall well-being.
In today’s fast-paced world, many of us spend hours working at desks, lifting heavy objects, or engaging in repetitive tasks. Without proper ergonomic practices, these activities can lead to discomfort, pain, and even long-term injuries. Fortunately, by incorporating ergonomics into our daily routine, we can significantly reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and improve overall well-being.
Understanding Ergonomics
Ergonomics is the science of designing workspaces, tools, and practices to fit the capabilities and limitations of the human body. It aims to enhance productivity while minimizing strain, discomfort, and injury. When applied correctly, ergonomics can help prevent common workplace issues such as carpal tunnel syndrome, back pain, and tendonitis.
Common Workplace Injuries and Their Causes
Many workplace injuries result from poor posture, repetitive movements, and inadequate workstation setups. Some common injuries include:

Practical Ergonomic Solutions
By making small adjustments to your workspace and daily habits, you can prevent injuries and improve comfort. Here are some key ergonomic strategies:
1. Optimize Your Workspace
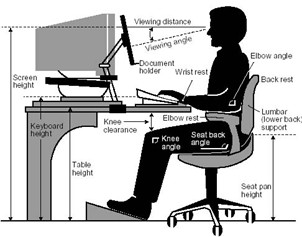 Position Your Screen Correctly: Keep your monitor at eye level and about an arm’s length away to prevent neck strain.
Position Your Screen Correctly: Keep your monitor at eye level and about an arm’s length away to prevent neck strain.2. Maintain Proper Posture
3. Incorporate Movement and Stretching
Small adjustments, such as optimizing your workstation, practicing good posture, and taking regular breaks, can make a significant impact on your well-being. By prioritizing ergonomics, you can work more comfortably, efficiently, and injury-free.
 Recovering from a workplace injury is not just about physical healing, it also requires active involvement from injured employees. Patient engagement is crucial in workers’ compensation cases, as it promotes better rehabilitation, shorter recovery times, and a smoother return to work. Employers, insurers, and healthcare providers must foster engagement by encouraging collaboration, communication, and personalized treatment plans. When injured workers take an active role in their recovery, they experience better health outcomes, reduced stress, and greater confidence in returning to work.
Recovering from a workplace injury is not just about physical healing, it also requires active involvement from injured employees. Patient engagement is crucial in workers’ compensation cases, as it promotes better rehabilitation, shorter recovery times, and a smoother return to work. Employers, insurers, and healthcare providers must foster engagement by encouraging collaboration, communication, and personalized treatment plans. When injured workers take an active role in their recovery, they experience better health outcomes, reduced stress, and greater confidence in returning to work.
Why Patient Engagement Matters
Patient engagement refers to the involvement of injured employees in their own treatment process, including understanding their condition, following medical advice, and making informed decisions about care. Actively engaged patients tend to:
Without engagement, workers may feel disconnected from their care, leading to delayed recovery and unnecessary medical costs.
Ways to Enhance Patient Engagement
1. Clear Communication and Education
 Many injured workers feel overwhelmed by medical terminology and unclear recovery expectations. Providing straightforward, accessible information empowers them to take control of their rehabilitation.
Many injured workers feel overwhelmed by medical terminology and unclear recovery expectations. Providing straightforward, accessible information empowers them to take control of their rehabilitation.
Strategies to improve communication include:
2. Personalized Recovery Plans
Since every workplace injury is unique, treatment plans should be tailored to individual needs. Customized care improves engagement by ensuring patients receive therapies suited to their physical condition, job role, and lifestyle.
Best practices include:
3. Digital Health Tools and Telemedicine
Technology can improve patient engagement by providing real-time recovery tracking, remote consultations, and automated reminders.
These digital tools help workers stay engaged by:
 Sending reminders for therapy sessions and medications.
Sending reminders for therapy sessions and medications.By making healthcare more accessible, technology removes barriers to engagement and helps workers stay committed to their recovery.
4. Workplace Support and Early Intervention
A supportive work environment can make a significant difference in engagement. Employers should focus on early intervention and accommodations to keep injured employees connected to their workplace throughout recovery.
Effective workplace support includes:
5. Collaboration Between Stakeholders
Patient engagement thrives when case managers, medical providers, and employers work together to guide injured workers through recovery. Coordination ensures that employees receive consistent care, guidance, and return-to-work planning.
Best practices for collaboration include:
 A well-coordinated approach reduces recovery delays, prevents complications, and improves long-term outcomes. Enhancing patient engagement during workers’ compensation recovery ensures better rehabilitation results, lower disability durations, and a smoother transition back to work. Clear communication, personalized treatment plans, digital health tools, workplace support, and collaboration all contribute to active participation in the healing process. With a proactive, patient-centered approach, injured workers regain confidence, recover more effectively, and return to work ready to succeed.
A well-coordinated approach reduces recovery delays, prevents complications, and improves long-term outcomes. Enhancing patient engagement during workers’ compensation recovery ensures better rehabilitation results, lower disability durations, and a smoother transition back to work. Clear communication, personalized treatment plans, digital health tools, workplace support, and collaboration all contribute to active participation in the healing process. With a proactive, patient-centered approach, injured workers regain confidence, recover more effectively, and return to work ready to succeed.
 Assessing permanent disability in complex case management is a crucial process that impacts injured individuals, employers, and insurance providers alike. Permanent disability refers to a lasting impairment that affects a person’s ability to work and perform daily activities. In workers’ compensation and healthcare settings, accurately evaluating the extent of a disability is essential to ensure fair compensation, appropriate medical care, and effective rehabilitation planning.
Assessing permanent disability in complex case management is a crucial process that impacts injured individuals, employers, and insurance providers alike. Permanent disability refers to a lasting impairment that affects a person’s ability to work and perform daily activities. In workers’ compensation and healthcare settings, accurately evaluating the extent of a disability is essential to ensure fair compensation, appropriate medical care, and effective rehabilitation planning.
Permanent disability occurs when an individual suffers an injury that does not fully heal, resulting in lasting physical or mental limitations. In the realm of complex medical case management, these disabilities are often associated with chronic conditions, severe injuries, or progressive diseases that impact a person’s ability to return to work at their previous capacity.
The Importance of Comprehensive Assessment
A thorough assessment of permanent disability ensures that affected individuals receive the correct benefits and medical care. In complex medical cases, where multiple factors contribute to a person’s condition, a multidisciplinary approach is required to accurately evaluate the severity of disability and its long-term effects.
Key components of permanent disability assessment include:
By integrating these assessments, case managers and healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding the disability rating and appropriate accommodation.
 Common Challenges in Assessing Permanent Disability
Common Challenges in Assessing Permanent Disability
· Complexity of Medical Conditions
In cases involving traumatic injuries, chronic illnesses, or multiple diagnoses, determining disability can be difficult. Individuals may experience fluctuating symptoms, making it challenging to assign a definitive disability rating.
Subjectivity in Pain and Impairment Levels
Pain perception and functional limitations vary among individuals. A person’s ability to cope with discomfort and adjust to disabilities can impact assessments, making it essential to rely on objective medical evidence.
Disputes Over Disability Ratings
 Employers, insurance providers, and injured individuals may contest disability ratings due to financial implications. These disputes often require additional medical opinions, legal mediation, or appeals processes.
Employers, insurance providers, and injured individuals may contest disability ratings due to financial implications. These disputes often require additional medical opinions, legal mediation, or appeals processes.
Regulatory Variations
Workers’ compensation laws and disability evaluation guidelines differ by state or country, complicating assessments. Case managers must stay informed about legal requirements to ensure compliance with local policies.
Key Methods for Disability Assessment
Functional Testing and Vocational Assessments
Evaluating an individual’s ability to perform work-related tasks is a critical component of disability assessment. Functional testing includes mobility evaluations, strength tests, and endurance measurements.
Vocational assessments determine whether the individual can return to their previous job or if accommodation is necessary. In cases where return-to-work is impossible, vocational rehabilitation services may be required to explore alternative employment options.
Independent Medical Exams (IME)
Employers and insurance providers may request an Independent Medical Exam (IME) to obtain an unbiased opinion from a healthcare provider who has not previously treated the patient. IMEs help resolve disputes and clarify disability classifications.
Long-Term Impacts of Permanent Disability
Permanent disability assessments extend beyond initial evaluations; they influence financial stability, healthcare planning, and lifestyle adjustments. Individuals who are deemed permanently disabled may require:
 Long-Term Medical Treatment: Including rehabilitation therapy and pain management.
Long-Term Medical Treatment: Including rehabilitation therapy and pain management.Conclusion
Assessing permanent disability in complex case management requires a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to ensure fair outcomes for injured individuals. By leveraging medical evaluations, functional assessments, legal expertise, and standardized rating systems, case managers can accurately determine impairment levels and provide appropriate benefits. Despite the challenges of disability assessment, thorough evaluations and collaboration among healthcare providers, insurers, and employers can facilitate better decision-making, helping individuals navigate their limitations while receiving the support they need.
 Workers’ compensation is designed to support employees who suffer job-related injuries or illnesses, providing medical care and financial assistance to aid recovery. While physical injuries are often the primary focus, behavioral health services play a crucial role in ensuring comprehensive care. Mental health challenges, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress, can develop alongside or because of workplace injuries, impacting recovery and return-to-work outcomes.
Workers’ compensation is designed to support employees who suffer job-related injuries or illnesses, providing medical care and financial assistance to aid recovery. While physical injuries are often the primary focus, behavioral health services play a crucial role in ensuring comprehensive care. Mental health challenges, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress, can develop alongside or because of workplace injuries, impacting recovery and return-to-work outcomes.
Understanding how behavioral health services integrate with workers’ compensation can improve outcomes for injured employees while reducing long-term costs for employers and insurers.
The Link Between Workplace Injuries and Mental Health
Workplace injuries can have far-reaching effects beyond physical harm. Employees who experience serious injuries often face stress, anxiety, or depression due to:
Pain and Physical Limitations – Chronic pain or permanent injuries can lead to emotional distress.
Financial Uncertainty – Wage loss and medical bills may contribute to anxiety.
Social Isolation – Limited mobility or extended recovery periods can impact relationships and social interactions.
Benefits of Behavioral Health Services in Workers’ Compensation
Enhancing Recovery and Return-to-Work Rates
 Mental health challenges can significantly impact recovery from physical injuries. Depression, anxiety, and stress can delay healing, reduce motivation to adhere to treatment plans, and make returning to work more difficult.
Mental health challenges can significantly impact recovery from physical injuries. Depression, anxiety, and stress can delay healing, reduce motivation to adhere to treatment plans, and make returning to work more difficult.
By addressing these concerns through behavioral health interventions, injured workers can; Build coping strategies to manage stress and anxiety, improve adherence to rehabilitation programs, and regain confidence in their ability to return to work.
Reducing Long-Term Disability and Costs
Untreated mental health issues can lead to long-term disability claims, increasing costs for employers and insurers. Employees who receive timely behavioral health support are more likely to recover successfully and resume work sooner. Employers benefit by lowering costs related to lost productivity, extended disability claims, and additional medical treatments.
Preventing Opioid Dependence and Substance Abuse
Many injured workers receive pain management treatments, which can include prescription medications such as opioids. Without behavioral health support, some employees may develop dependence, leading to substance abuse issues.
Behavioral health services provide:
 Alternatives to opioid use, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for pain management.
Alternatives to opioid use, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for pain management.Addressing Workplace Trauma and PTSD
Certain jobs, such as first responders, healthcare workers, and construction professionals, expose employees to potentially traumatic events. Workplace injuries, serious accidents, or witnessing distressing situations can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Behavioral health professionals can provide specialized trauma-informed care, ensuring affected employees receive appropriate interventions, including therapy and stress management strategies.
Key Behavioral Health Services in Workers’ Compensation
To ensure comprehensive care, workers’ compensation programs can integrate various behavioral health services, including:
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Provides coping mechanisms for stress, anxiety, and pain management.

Vocational Rehabilitation Counseling – Supports workers adjusting to new roles due to injury-related limitations.
Behavioral health services are a critical component of workers’ compensation, ensuring injured employees receive holistic care that addresses both physical and psychological well-being. By incorporating mental health interventions, employers and insurers can improve recovery outcomes, reduce long-term disability claims, and foster a more supportive workplace environment. As awareness grows, integrating behavioral health services into workers’ compensation programs will continue to evolve, leading to better rehabilitation, lower costs, and healthier employees.
In the realm of public agencies, the symbiosis of workers’
compensation and safety practices represents a frontier of untapped potential
in fostering organizational resilience. Resilience, in this context, refers to
an agency’s ability to anticipate, respond, and adapt to challenges—ranging
from workplace accidents to large-scale emergencies—while maintaining
continuous operations. Strategically merging these domains can bolster
resilience, improve employee welfare, and streamline operations within public
agencies.
 Traditionally,
Traditionally,
workers’ compensation and safety efforts have operated in silos. Compensation
policies react post-incident, dealing with the aftermath of accidents, while
safety programs strive to be proactive, with a focus on prevention. This
separation can result in inefficiencies, missed opportunities for improvement,
and increased costs—both human and financial. A more integrated approach can
address these gaps by aligning objectives, resources, and information systems.
The Benefits of Integration
1. Enhanced Risk Management: By uniting safety and workers’
compensation efforts, agencies can develop more holistic risk management
strategies. Combined data from both fields provides deeper insights into the
potential hazards, trends in incidents, and the effectiveness of safety
interventions.
 2. Improved Incident
2. Improved Incident
Response and Recovery: Integrated systems facilitate quicker, more coordinated
responses to workplace incidents. When safety protocols and compensation
procedures are aligned, agencies can ensure that affected employees receive
immediate care, which can lead to quicker recovery times and reduced downtime.
3. Cost Efficiency: Merging these programs can lead to
significant cost savings. With a unified strategy, agencies can reduce
redundancy in administrative tasks, streamline training programs, and minimize
the financial impact of workplace injuries through enhanced preventative
measures.
4. Boosted Employee Morale and Productivity: A culture that
prioritizes safety and well-being, manifested through cohesive policies, can
enhance worker satisfaction and productivity. Employees are more likely to
engage in their work and remain committed to an organization that actively
promotes a safe working environment and supports them in times of need.
 5. Compliance and
5. Compliance and
Reputation: Integrated safety and compensation practices help ensure regulatory
compliance, reducing the risk of fines and sanctions. Moreover, they enhance an
agency’s reputation as a responsible and caring employer, which is crucial in
attracting and retaining talent.
Strategies for integration need
to include:
Leadership and Culture
Collaborative Policy
Development
Unified Data Systems
Cross-Functional Teams
While integration offers numerous
benefits, it also presents challenges. Resistance to change, budget
constraints, and the complexity of aligning different departmental processes
can hinder progress. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning,
stakeholder engagement, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Opportunities
abound in leveraging technology and innovation. The advent of digital
platforms, wearable safety devices, and AI-driven analytics can further enhance
the integration process, providing real-time insights and streamline
operations.
The integration of workers’ compensation and safety within
public agencies is more than a bureaucratic adjustment; it’s a paradigm shift
towards resilience and sustainability. By embracing this holistic approach,
agencies can safeguard their most valuable assets—their people—while ensuring
operational efficiency and adaptability in a complex, ever-changing world.
California is stirring with legislative changes that promise to redefine the workers’ compensation landscape. California has always been a pioneering state when it comes to employee rights and workers’ compensation, and the new wave of legislative updates slated for implementation in 2025 are set to cement this reputation. The following is an overview of the key legislative changes for 2025, their implications for employers and employees, and how these adjustments will influence the broader workers’ compensation ecosystem.
Key Legislative Updates

Enhanced Medical Treatment Guidelines- One of the most significant changes in 2025 is the update to medical treatment guidelines. The aim is to streamline the medical review process, making it more responsive and efficient. By adopting evidence-based guidelines updated with the latest medical research, the legislation intends to ensure injured workers receive timely and appropriate care, potentially reducing litigation over treatment disputes.
Mental Health and Stress-Related Claims- Recognizing the increasing importance of mental health, the 2025 updates will expand coverage for mental health and stress-related claims. Under the new regulations, conditions such as depression and anxiety stemming from workplace incidents will be eligible for compensation. This change underscores California’s commitment to comprehensive worker health, acknowledging that injuries are not solely physical.
Technology and Telehealth Reforms- With the digital shift accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth services have become a critical component of healthcare delivery. The 2025 legislation formalizes the role of telehealth in workers’ compensation claims, ensuring that virtual consultations and treatment are recognized and reimbursed. By embracing technology, the new rules aim to increase access to care, especially for workers in remote areas.

Revised Disability Rating System- The legislation introduces reforms to the Permanent Disability Rating Schedule (PDRS). The revised system will utilize a more nuanced approach to assess and rate disabilities, accounting for advancements in medical care and rehabilitation. This update is intended to provide fairer compensation that more accurately reflects the true impact of injuries on workers’ lives.
Focus on Preventive Measures- A proactive approach to workplace safety and injury prevention is at the heart of the 2025 updates. The regulations encourage employers to adopt comprehensive safety programs, conduct regular risk assessments, and provide employee training. Incentives for businesses that demonstrate exemplary safety records are also part of the new framework, illustrating a shift towards prevention rather than mere compensation post-incident.
Clean Energy Sector Specific Rules- As California leads the charge towards renewable energy, the 2025 legislation includes specific provisions for the rapidly growing clean energy sector. These rules address unique risks associated with renewable energy production and installation, ensuring that workers in this vital industry are adequately protected.
Implications for Employees
 Employees stand to benefit significantly from the 2025 updates. The broader inclusion of mental health claims acknowledges the complex nature of workplace injuries and provides a more comprehensive safety net. Streamlined medical treatments and the embrace of telehealth mean quicker, more convenient access to necessary care. Additionally, the revised disability rating system promises fairer compensation for affected workers, reflecting a more accurate understanding of disabilities’ long-term impacts.
Employees stand to benefit significantly from the 2025 updates. The broader inclusion of mental health claims acknowledges the complex nature of workplace injuries and provides a more comprehensive safety net. Streamlined medical treatments and the embrace of telehealth mean quicker, more convenient access to necessary care. Additionally, the revised disability rating system promises fairer compensation for affected workers, reflecting a more accurate understanding of disabilities’ long-term impacts.
With these sweeping changes on the horizon, stakeholders in California’s workers’ compensation system—employers, employees, insurers, and healthcare providers—must prepare for the transition. Open communication, ongoing education, and strategic planning will be crucial in adapting to the new rules and leveraging them for improved workplace health and safety.
 The landscape of
workers’ compensation rehabilitation is constantly evolving, seeking innovative
strategies to optimize recovery outcomes and minimize the long-term impact of
workplace injuries. One emerging area of interest is the integration of weight
loss medications into rehabilitation programs, driven by a growing body of
evidence linking obesity to prolonged disability and increased healthcare
costs. This article delves into the complex considerations surrounding this
approach, examining its potential benefits, challenges, and ethical
implications.
The landscape of
workers’ compensation rehabilitation is constantly evolving, seeking innovative
strategies to optimize recovery outcomes and minimize the long-term impact of
workplace injuries. One emerging area of interest is the integration of weight
loss medications into rehabilitation programs, driven by a growing body of
evidence linking obesity to prolonged disability and increased healthcare
costs. This article delves into the complex considerations surrounding this
approach, examining its potential benefits, challenges, and ethical
implications.
The Burden of Obesity in Workplace Injuries and Rehabilitation
Traditionally, workers’ compensation rehabilitation has primarily focused on physical therapy, medical treatments, and surgical interventions. However, the significant influence of obesity as a comorbid factor has prompted a shift towards more holistic approaches that address underlying health conditions impacting recovery. Obesity is increasingly recognized as a major contributor to workplace injuries and a significant impediment to successful rehabilitation.
Studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between obesity and a higher incidence of workplace injuries, particularly musculoskeletal disorders. Excess weight places additional stress on joints, ligaments, and muscles, increasing the risk of strains, sprains, and other injuries. Moreover, obesity is often associated with other health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea, which can further complicate recovery and prolong disability.
 Overweight and obese
individuals often experience longer recovery times, higher rates of re-injury,
and a greater likelihood of permanent disability following a workplace injury.
This translates into increased healthcare costs, lost productivity, and a diminished
quality of life for injured workers. Incorporating comprehensive weight
management strategies, including the potential use of weight loss medications,
into rehabilitation plans offers a promising avenue for mitigating these risks
and promoting more effective and sustainable recovery.
Overweight and obese
individuals often experience longer recovery times, higher rates of re-injury,
and a greater likelihood of permanent disability following a workplace injury.
This translates into increased healthcare costs, lost productivity, and a diminished
quality of life for injured workers. Incorporating comprehensive weight
management strategies, including the potential use of weight loss medications,
into rehabilitation plans offers a promising avenue for mitigating these risks
and promoting more effective and sustainable recovery.
The Potential Benefits of Weight Loss Medications in Rehabilitation
The strategic use of weight loss medications in the context of a comprehensive rehabilitation program can offer several potential advantages:
 Reduction in
Comorbid Conditions:
Effective weight management, supported by
medication if appropriate, can contribute to the improvement or remission
of obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
Managing these comorbidities is crucial for optimizing overall health and
facilitating a smoother rehabilitation process.
Reduction in
Comorbid Conditions:
Effective weight management, supported by
medication if appropriate, can contribute to the improvement or remission
of obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
Managing these comorbidities is crucial for optimizing overall health and
facilitating a smoother rehabilitation process.Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits are significant, integrating weight loss medications into workers’ compensation rehabilitation requires careful consideration of several factors:
 Cost-Effectiveness
Analysis:
While weight loss medications represent an upfront
cost, their potential to reduce long-term healthcare expenses and lost
productivity needs to be carefully evaluated. Cost-benefit analyses should
be conducted to assess the overall economic impact of incorporating these
medications into rehabilitation programs.
Cost-Effectiveness
Analysis:
While weight loss medications represent an upfront
cost, their potential to reduce long-term healthcare expenses and lost
productivity needs to be carefully evaluated. Cost-benefit analyses should
be conducted to assess the overall economic impact of incorporating these
medications into rehabilitation programs.Looking Ahead: A Multidisciplinary Approach
The successful integration of weight loss medications into workers’ compensation rehabilitation requires a collaborative, multidisciplinary approach. Physicians, rehabilitation specialists, dietitians, psychologists, and other healthcare professionals need to work together to develop individualized treatment plans that address the unique needs of each injured worker.
Navigating the intricate maze of healthcare and insurance can often be a daunting task, particularly when dealing with work-related injuries. However, the intersection of Medicare and workers’ compensation can often lead to questions and complexities. We’ll explore this intersection, clarify key concepts, and discuss how Medicare interacts with workers’ compensation claims.
How Medicare Interacts with Workers’ Compensation
 Medicare and workers’ compensation often intersect when an individual eligible for Medicare suffers a work-related injury. The way Medicare and workers’ compensation coordinate can have significant implications for both coverage and financial responsibility.
Medicare and workers’ compensation often intersect when an individual eligible for Medicare suffers a work-related injury. The way Medicare and workers’ compensation coordinate can have significant implications for both coverage and financial responsibility.
Primary vs. Secondary Payer
In cases where Medicare and workers’ compensation both provide coverage, workers’ compensation is always the primary payer. This means workers’ compensation must cover medical expenses related to the workplace injury before Medicare steps in as a secondary payer. Medicare will only pay for services if they are not covered by workers’ compensation.
Medicare Set-Aside (MSA) Accounts
One of the most critical aspects of coordinating Medicare and workers’ compensation is the Medicare Set-Aside (MSA) arrangement. An MSA is an allocated sum of money set aside to cover future medical expenses related to a workplace injury that would otherwise be covered by Medicare. The purpose of an MSA is to ensure that Medicare does not pay for costs that should be covered by workers’ compensation.
Conditional Payments
 Sometimes, Medicare may make conditional payments for work-related injuries. These are payments that Medicare makes on the condition that it will be reimbursed once the workers’ compensation claim is settled. Failure to address these conditional payments can lead to substantial penalties and recovery actions by Medicare.
Sometimes, Medicare may make conditional payments for work-related injuries. These are payments that Medicare makes on the condition that it will be reimbursed once the workers’ compensation claim is settled. Failure to address these conditional payments can lead to substantial penalties and recovery actions by Medicare.
Several legal frameworks govern the interaction between Medicare and workers’ compensation. The Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) statute is critical in this context. It mandates that Medicare is secondary to workers’ compensation and other primary plans. Non-compliance with MSP rules can result in hefty penalties and litigation. Understanding how Medicare interacts with workers’ compensation is essential for injured workers, employers, insurers, and healthcare providers.  The primary vs. secondary payer principle, the importance of MSAs, the role of conditional payments, and the need for coordination and compliance form the bedrock of this interaction. The integration of Medicare with workers’ compensation represents a commitment to ensuring that injured workers receive comprehensive, timely, and financially responsible medical care, enabling them to return to their lives and careers with confidence.
The primary vs. secondary payer principle, the importance of MSAs, the role of conditional payments, and the need for coordination and compliance form the bedrock of this interaction. The integration of Medicare with workers’ compensation represents a commitment to ensuring that injured workers receive comprehensive, timely, and financially responsible medical care, enabling them to return to their lives and careers with confidence.
Artificial Intelligence encompasses a myriad of applications in medicine, including predictive analytics, personalized treatment plans, medical imaging, and robotic surgeries. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data faster and more accurately than human counterparts, leading to early diagnosis of diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Personalized medicine, driven by A.I., offers customized treatment plans tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup, leading to improved patient outcomes.
The Regulatory Landscape
 To harness the potential of A.I. in medicine while safeguarding public health, various international regulatory bodies have started formulating policies and frameworks. The primary objective is to ensure that A.I. systems are developed responsibly and function safely within the medical domain.
To harness the potential of A.I. in medicine while safeguarding public health, various international regulatory bodies have started formulating policies and frameworks. The primary objective is to ensure that A.I. systems are developed responsibly and function safely within the medical domain.
In the U.S., the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in A.I. regulation. The FDA has developed a framework for evaluating A.I. and Machine Learning (ML) medical devices through a risk-based approach. Devices are categorized based on their potential risk to patients, influencing the level of scrutiny and premarket approval. The FDA also emphasizes the importance of transparency, requiring manufacturers to disclose algorithm changes and ensure continuous monitoring.
Ethical Considerations
The adoption of A.I. in medicine is accompanied by several ethical concerns that must be addressed through robust legislation and regulations. A.I. systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in training data, leading to unfair treatment outcomes. Ensuring fairness requires stringent regulations mandating the use of diverse and representative datasets. Patients and healthcare providers must be able to understand and trust A.I. systems. Regulations should enforce transparency, requiring developers to explain how algorithms work and how decisions are made. Accountability mechanisms must be in place to address any harm caused by A.I.-driven decisions.
 The use of A.I. in healthcare involves the processing of sensitive personal data. Legislations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU set stringent guidelines for data protection. Ensuring data security and patient privacy is paramount to maintain public trust. The integration of A.I. should enhance, rather than undermine, the doctor-patient relationship. Legislation should ensure that A.I. serves as a tool to support healthcare professionals, preserving the humane aspect of medical practice.
The use of A.I. in healthcare involves the processing of sensitive personal data. Legislations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU set stringent guidelines for data protection. Ensuring data security and patient privacy is paramount to maintain public trust. The integration of A.I. should enhance, rather than undermine, the doctor-patient relationship. Legislation should ensure that A.I. serves as a tool to support healthcare professionals, preserving the humane aspect of medical practice.
Future Directions
The integration of A.I. into medicine holds immense potential to revolutionize healthcare, but it is accompanied by significant ethical, legal, and regulatory challenges.  Developing and implementing effective legislation and regulations is essential to ensure that A.I. advancements contribute positively to medical practice, safeguarding patient safety and promoting equitable and high-quality care. The journey towards robust A.I. regulation in medicine is complex, requiring continuous collaboration, innovation, and vigilance. By navigating this dynamic landscape thoughtfully, we can harness the transformative power of A.I. to advance the future of healthcare.
Developing and implementing effective legislation and regulations is essential to ensure that A.I. advancements contribute positively to medical practice, safeguarding patient safety and promoting equitable and high-quality care. The journey towards robust A.I. regulation in medicine is complex, requiring continuous collaboration, innovation, and vigilance. By navigating this dynamic landscape thoughtfully, we can harness the transformative power of A.I. to advance the future of healthcare.
Chronic pain is a pervasive and often debilitating condition affecting millions of people globally. It can stem from various causes, including injuries, surgeries, medical conditions like arthritis, and nerve damage. Managing chronic pain effectively is crucial for enhancing patients’ quality of life and functional capacity. A significant aspect of chronic pain management is pharmacy utilization, which encompasses the appropriate and strategic use of medications to alleviate pain while minimizing adverse effects and the risk of dependency. This blog delves into the intricacies of pharmacy utilization for chronic pain cases, offering insights into medication options, best practices, and the importance of a multidisciplinary approach. Pharmacy utilization in chronic pain management involves the use of various medications, each with specific indications, mechanisms of action, and potential side effects. The goal is to achieve optimal pain relief while mitigating risks associated with long-term medication use.
A significant aspect of chronic pain management is pharmacy utilization, which encompasses the appropriate and strategic use of medications to alleviate pain while minimizing adverse effects and the risk of dependency. This blog delves into the intricacies of pharmacy utilization for chronic pain cases, offering insights into medication options, best practices, and the importance of a multidisciplinary approach. Pharmacy utilization in chronic pain management involves the use of various medications, each with specific indications, mechanisms of action, and potential side effects. The goal is to achieve optimal pain relief while mitigating risks associated with long-term medication use.
Best Practices for Pharmacy Utilization in Chronic Pain Cases
Effective pharmacy utilization in chronic pain management requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating best practices to ensure safety, efficacy, and patient engagement.
Comprehensive Assessment– A thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history, pain characteristics, and previous treatments is crucial. This helps tailor a personalized pain management plan and identify potential contraindications for certain medications.
Incremental Approach– Start with the least invasive options and escalate as necessary. Begin with non-opioid analgesics and adjuvant medications before considering opioids. This minimizes the risk of dependency and side effects.

Patient Education– Educating patients about their medications, including how to use them correctly, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence, is essential. Informed patients are more likely to engage actively in their pain management and report any issues promptly.
Regular Monitoring– Regular follow-ups are vital to assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan, monitor for side effects, and adjust medications as needed. This is particularly important for patients on opioids to prevent addiction and misuse.
Multidisciplinary Approach– Integrating other modalities such as physical therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and lifestyle modifications can enhance the overall effectiveness of pain management. A collaborative approach involving healthcare providers from various disciplines ensures comprehensive care.
Pharmacy utilization is a cornerstone of chronic pain management, offering a range of medications to alleviate pain and improve patients’ quality of life. However, it requires a balanced approach that considers efficacy, safety, and the potential for abuse. A comprehensive assessment, incremental treatment approach, patient education, regular monitoring, and a multidisciplinary strategy are essential components of effective pain management. Addressing the challenges and complexities associated with chronic pain medications ensures that patients receive the best possible care, making it possible to manage pain effectively while minimizing risks. By embracing a holistic and patient-centered approach, healthcare providers can navigate the complexities of pharmacy utilization for chronic pain cases, improving outcomes and enhancing the overall well-being of patients.
A comprehensive assessment, incremental treatment approach, patient education, regular monitoring, and a multidisciplinary strategy are essential components of effective pain management. Addressing the challenges and complexities associated with chronic pain medications ensures that patients receive the best possible care, making it possible to manage pain effectively while minimizing risks. By embracing a holistic and patient-centered approach, healthcare providers can navigate the complexities of pharmacy utilization for chronic pain cases, improving outcomes and enhancing the overall well-being of patients.
Workers’ compensation aims to provide timely and effective medical care for employees who sustain work-related injuries. As the workforce and job requirements evolve, so do the nature and complexity of workplace injuries. One significant advancement in the medical field that has had a profound impact on workers’ compensation is the use of surgical implants. These implants play a crucial role in restoring function and accelerating recovery for injured workers, helping them return to their jobs more quickly and reducing the overall costs for employers and insurers.
Types of Surgical Implants in Workers’ Comp
Orthopedic Implants: Among the most common are knee and hip replacements, plates, screws, and rods used to stabilize fractures and dislocations.  These implants can significantly improve mobility and reduce pain, allowing workers to regain function more quickly.
These implants can significantly improve mobility and reduce pain, allowing workers to regain function more quickly.
Spinal Implants: Used to treat conditions such as herniated discs or spinal fractures, these include rods, cages, and artificial discs. They help stabilize the spine and relieve nerve pressure, which can alleviate chronic pain and improve physical capabilities.
Dental and Cranial Implants: For workers who suffer facial or cranial injuries, implants can help restore not just function but also appearance.  Dental implants, for example, can replace lost teeth, while cranial implants can repair skull fractures.
Dental implants, for example, can replace lost teeth, while cranial implants can repair skull fractures.
Enhanced Recovery: The most significant advantage of surgical implants is the enhancement of recovery times. Injured workers benefit from modern surgical techniques and implants by restoring function faster than traditional treatments. For example, an individual with a severe knee injury might have faced a prolonged disability period. However, with a knee replacement implant, they can regain their mobility and return to work sooner.
Reduction in Long-term Disability: Employers often face substantial costs associated with long-term disability. Surgical implants can mitigate these costs by reducing the likelihood of chronic conditions that necessitate extended leave or permanent disability. Improved mobility and pain reduction translate to less time away from work and fewer long-term health complications.
Cost Efficiency: While surgical implants may have a high upfront cost, their long-term financial benefits can be substantial. The reduced recovery times and enhanced healing translate to fewer extended care requirements, less physical therapy, and reduced need for prolonged medication. Additionally, a faster return to work means employees can continue to contribute to productivity, offsetting the initial medical expenses.
Improved Quality of Life: For the injured workers, the use of surgical implants often means a better quality of life. The restoration of function and reduction of pain enables them to return not only to their professional duties but also to their daily activities without significant limitations. This psychological and physical well-being is invaluable.
 Incorporating surgical implants into the workers’ compensation framework is not just a medical advancement; it’s a commitment to improving patient outcomes and fostering a more efficient and compassionate approach to workplace injury recovery. By investing in these technologies, we pave the way for a healthier, more productive workforce, benefiting both employees and employers alike.
Incorporating surgical implants into the workers’ compensation framework is not just a medical advancement; it’s a commitment to improving patient outcomes and fostering a more efficient and compassionate approach to workplace injury recovery. By investing in these technologies, we pave the way for a healthier, more productive workforce, benefiting both employees and employers alike. In today’s dynamic and fast-paced work environment, the prevention of workplace injuries is of paramount importance. Companies invest heavily in safety protocols, training, and equipment to protect their workforce. Despite these measures, workplace injuries remain prevalent, leading to significant financial and operational burdens. Enter wearable technology—a revolutionary tool that has the potential to transform workplace safety and reduce workers’ compensation claims. This blog explores the value of wearables in preventing workers’ compensation injuries, outlining the benefits, types of devices, case studies, and future directions.
Understanding Wearable Technology
Wearable technology refers to electronic devices that are worn on the body, either as accessories or embedded in clothing. These devices often include sensors that collect and transmit data in real-time. In the context of workplace safety, wearables can monitor a variety of physiological and environmental parameters, providing valuable insights that can prevent accidents and injuries. Some examples of wearable technologies are fitness trackers and smartwatches, smart clothing, Augmented Reality (AR) glasses, exoskeletons, and environmental sensors.
These devices often include sensors that collect and transmit data in real-time. In the context of workplace safety, wearables can monitor a variety of physiological and environmental parameters, providing valuable insights that can prevent accidents and injuries. Some examples of wearable technologies are fitness trackers and smartwatches, smart clothing, Augmented Reality (AR) glasses, exoskeletons, and environmental sensors.
Benefits of Wearables in Preventing Workplace Injuries
One of the most significant advantages of wearables is their ability to provide real-time monitoring and alerts. Sensors constantly collect data on a worker’s physical condition and the environment, enabling immediate interventions when abnormal conditions are detected. For instance, if a construction worker’s heart rate spikes or if they exhibit signs of heat stress, the wearable device can alert the individual and their supervisor, prompting timely action to prevent an incident. The data collected by wearables can be analyzed to identify patterns and trends in workplace safety. This information can be used to optimize safety protocols, design better training programs, and make informed decisions about workplace modifications. For example, if data shows that a particular task is associated with a high incidence of lower back injuries, employers can redesign the workflow or introduce assistive devices to reduce the risk.
For instance, if a construction worker’s heart rate spikes or if they exhibit signs of heat stress, the wearable device can alert the individual and their supervisor, prompting timely action to prevent an incident. The data collected by wearables can be analyzed to identify patterns and trends in workplace safety. This information can be used to optimize safety protocols, design better training programs, and make informed decisions about workplace modifications. For example, if data shows that a particular task is associated with a high incidence of lower back injuries, employers can redesign the workflow or introduce assistive devices to reduce the risk.
Future Directions
The adoption of wearable technology in workplace safety is still in its early stages, but the potential for growth is immense. The integration of wearables with the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) could revolutionize workplace safety. IoT connectivity allows data from multiple devices to be aggregated and analyzed, providing comprehensive insights into workplace safety. AI algorithms can predict potential safety hazards and suggest proactive measures to mitigate risks. As wearable technology continues to evolve, we can expect more customizable solutions tailored to specific industries and job roles. For example, wearables designed for the construction industry may focus on ergonomics and environmental hazards, while those for healthcare workers might prioritize fatigue management and infection control.
 Wearable technology holds immense potential for preventing workers’ compensation injuries and enhancing workplace safety. By providing real-time monitoring, promoting better ergonomics, managing fatigue and stress, and generating data-driven insights, wearables can significantly reduce the incidence of workplace injuries. As technology continues to advance, the integration of wearables with IoT and AI, along with the development of advanced biometrics and customizable solutions, will further revolutionize workplace safety.
Wearable technology holds immense potential for preventing workers’ compensation injuries and enhancing workplace safety. By providing real-time monitoring, promoting better ergonomics, managing fatigue and stress, and generating data-driven insights, wearables can significantly reduce the incidence of workplace injuries. As technology continues to advance, the integration of wearables with IoT and AI, along with the development of advanced biometrics and customizable solutions, will further revolutionize workplace safety.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital world, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a game-changing technology, creating waves across numerous industries. Among these, workers’ compensation case management stands as a prime example of a sector reaping profound benefits from RPA’s implementation. RPA involves deploying “bots” or software robots to automate repetitive and routine tasks previously performed by humans. In the context of workers’ compensation case management, these tasks include data entry, claims processing, and report generation, among others.
One of the most direct ways that  RPA improves workers’ compensation management is by significantly reducing the time taken to process claims. Automation alleviates the need for claim handlers to manually enter information into disparate systems – a process which is not only labor-intensive but also prone to human error. By automating these tasks, the claims process becomes quicker, more accurate, and allows human employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
RPA improves workers’ compensation management is by significantly reducing the time taken to process claims. Automation alleviates the need for claim handlers to manually enter information into disparate systems – a process which is not only labor-intensive but also prone to human error. By automating these tasks, the claims process becomes quicker, more accurate, and allows human employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
Fraud detection is another area of workers’ compensation case management where RPA shines. Detecting potential fraudulent cases traditionally requires sifting through vast data sets to identify discrepancies, a burdensome task when done manually. RPA, when paired with predictive analysis techniques, can boost this process by automatically flagging suspicious transactions. This early identification saves resources and prevents monetary losses from fraudulent claims.
 Amid the digital transformation era, harnessing technologies like RPA can unlock tremendous efficiency gains. By automating repetitive and systematic tasks, errors are reduced, and processing speeds increased. With the flexibility to scale as required, RPA can meet the demands posed by peak periods without overburdening human staff.
Amid the digital transformation era, harnessing technologies like RPA can unlock tremendous efficiency gains. By automating repetitive and systematic tasks, errors are reduced, and processing speeds increased. With the flexibility to scale as required, RPA can meet the demands posed by peak periods without overburdening human staff.
As the world becomes ever more digitized and interconnected, the treasure trove of data, securely stored in virtual servers, continues to grow exponentially.  Businesses, governments, and industries are finding more innovative ways to harness this data. One area that is experiencing a paradigm shift, thanks to data analytics, is worker’s compensation. Data analytics is transforming the management of worker’s compensation through the development of proactive strategies, delivering efficiencies, and improved outcomes for injured workers.
Businesses, governments, and industries are finding more innovative ways to harness this data. One area that is experiencing a paradigm shift, thanks to data analytics, is worker’s compensation. Data analytics is transforming the management of worker’s compensation through the development of proactive strategies, delivering efficiencies, and improved outcomes for injured workers.
Traditionally, the worker’s compensation landscape was marred by inefficient handling of claims, miscommunications, and fraudulent activities, all leading to financial drainage for companies and insufficient attention to injured workers. The advent of data analytics has brought a unique solution to these issues. One of the most promising ways data analytics is transforming workers’ compensation is predictive modeling.  Predictive models use historical data to anticipate future events. When applied to worker’s compensation, these models can anticipate the likelihood of an accident occurring in a particular job type, estimate the expected recovery time, or even predict the possibility of claim fraud. By knowing what is likely to happen, decision-makers can put in place proactive measures to minimize risk and manage consequences efficiently.
Predictive models use historical data to anticipate future events. When applied to worker’s compensation, these models can anticipate the likelihood of an accident occurring in a particular job type, estimate the expected recovery time, or even predict the possibility of claim fraud. By knowing what is likely to happen, decision-makers can put in place proactive measures to minimize risk and manage consequences efficiently.
For instance, understanding that certain job roles have a higher risk of specific injuries, companies can enhance safety training for those roles or improve safety equipment. Likewise, knowing that a particular claim has a high probability of being fraudulent, further investigation can be initiated, ensuring resources are not misused. While the implementation of data analytics in the management of workers’ compensation can be challenging, requiring both technological and cultural shifts in how businesses operate, it offers significant benefits. From cost savings through predictive modeling and fraud detection to enhanced worker well-being and improved communication, the role of data analytics in transforming workers’ compensation is powerful and far-reaching.
 As we continue to move further into the digital age, the influence of data analytics on industries like worker’s compensation cannot be underestimated. The invisible hand of this innovative tool, when correctly implemented, will continue to guide, and evolve the industry, leading to a more efficient, fair, and worker-friendly landscape.
As we continue to move further into the digital age, the influence of data analytics on industries like worker’s compensation cannot be underestimated. The invisible hand of this innovative tool, when correctly implemented, will continue to guide, and evolve the industry, leading to a more efficient, fair, and worker-friendly landscape.
In the wake of COVID-19, the world has drastically changed, and businesses have had to adapt to the new norm of remote work and digital tools. 
Telemedicine has emerged as a revolutionary solution in the management of worker’s compensation cases. The need to provide medical care while adhering to social distancing guidelines imposed by the pandemic led many businesses to pivot towards remote healthcare. This step brought about increased accessibility, convenience, and a reduced need for hospital visits, especially for follow-up care. Additionally, it eradicated geographical barriers, allowing injured workers to seek the best possible care from specialists, regardless of their location.
Additionally, drones are being harnessed more widely across industries, including workers’ compensation. In certain hazardous industries, such as construction or roofing, drones can provide remote evaluations of a work site post-incident, ensuring no further harm comes to workers. Additionally, drones can be used to assess situations and gauge safety measures, providing essential data without exposing workers to harmful conditions.
 These technological advancements have also necessitated modern companies to consider cyber risk management while handling sensitive worker data. As such, cybersecurity measures are an integral part of the tech-driven approach to worker’s compensation.
These technological advancements have also necessitated modern companies to consider cyber risk management while handling sensitive worker data. As such, cybersecurity measures are an integral part of the tech-driven approach to worker’s compensation.
In conclusion, the post-COVID-19 era has indeed significantly impacted worker’s compensation, necessitating a pivot toward technology like never before. The power of telemedicine, data analytics, AI, wearables, blockchain, drones, and cybersecurity, all contribute towards creating a faster, fairer, and more efficient workers’ compensation process. This shift is not just a response to the pandemic, but it presents a sustainable model that companies can and should consider for the future of worker’s compensation management. The growing role of technology in worker’s comp cases is rapidly reshaping the industry, serving as a reminder that even during immense challenge and change, innovation can still bloom.
 As the complexity of the digitized workplace surges, so does the demand for innovative methods to streamline and optimize the vast field of Worker’s Compensation. Amidst the myriad of emerging technological advancements, Predictive Modeling stands out as a game-changing tool that possesses potential to redefine Worker’s Compensation Case Management. Predictive Modeling is a process that uses data and statistical algorithms to ascertain the likelihood of future outcomes. In the scope of Worker’s Compensation, it harnesses data to generate predictions about future claims outcomes. The development, training, and implementation of these predictive models can facilitate early identification of high-risk cases, ensure quick resolution, decrease litigation rates, and ultimately reduce cost. It operates on the premise that historical claim data coupled with dynamic data inputs can provide valuable indicators of future claim developments.
As the complexity of the digitized workplace surges, so does the demand for innovative methods to streamline and optimize the vast field of Worker’s Compensation. Amidst the myriad of emerging technological advancements, Predictive Modeling stands out as a game-changing tool that possesses potential to redefine Worker’s Compensation Case Management. Predictive Modeling is a process that uses data and statistical algorithms to ascertain the likelihood of future outcomes. In the scope of Worker’s Compensation, it harnesses data to generate predictions about future claims outcomes. The development, training, and implementation of these predictive models can facilitate early identification of high-risk cases, ensure quick resolution, decrease litigation rates, and ultimately reduce cost. It operates on the premise that historical claim data coupled with dynamic data inputs can provide valuable indicators of future claim developments.
 The first huge advantage of predictive modeling in workers’ compensation is its ability to identify high-risk claims early. Traditional methods of identification relied on humans, who are subject to errors and inconsistencies. Predictive modeling can automatically identify high-risk cases, allowing case managers to prioritize them. Furthermore, it can identify which factors contribute to the high-risk nature, providing an opportunity to address and mitigate those risks promptly.
The first huge advantage of predictive modeling in workers’ compensation is its ability to identify high-risk claims early. Traditional methods of identification relied on humans, who are subject to errors and inconsistencies. Predictive modeling can automatically identify high-risk cases, allowing case managers to prioritize them. Furthermore, it can identify which factors contribute to the high-risk nature, providing an opportunity to address and mitigate those risks promptly.
A secondary key advantage is optimizing claim handling processes. Major pain points like administrative delays, repetitive tasks, and miscommunication can be significantly reduced. The technology uses historical data patterns to ascertain the most suitable course of action, enabling case workers to focus on the critical aspects of handling the claims.
 Lastly, Predictive Modeling uses Real-Time Analytics to continuously learn from new data inputs, significantly improving decision-making efficiency over time. As more data becomes available, the predictive power of the model improves, providing increasingly accurate forecasts.
Lastly, Predictive Modeling uses Real-Time Analytics to continuously learn from new data inputs, significantly improving decision-making efficiency over time. As more data becomes available, the predictive power of the model improves, providing increasingly accurate forecasts.
As organizations continue to refine their processes and strategies, it’s inevitable that this technologically advanced tool will form part of the future landscape for managing Workers’ Compensation cases. As we navigate the path to Worker’s Compensation Case Management refinement, Predictive Modeling serves as a beacon of promise, illuminating how we can enhance productivity, management, and decision making, all while ensuring the worker’s journey through these processes becomes more efficient and less distressing. It represents an exciting dimension of the technologically infused future of Worker’s Compensation.
At SCM Associates, our team of experienced nurses is dedicated to understanding the complexities that occur in a patient ‘s life due to an injury or illness. We place educating, coordination, and the implementation of winning solutions for patients at the forefront of our decision-making processes. Our team is more than just a case management company, we seek to provide expert, individualized solutions that focus on the wellbeing of each client. For more information, or to refer a case, please visit us at www.scmassociates.org/contact-us or call (562) 866-5162.
Injured workers face not only physical challenges but also mental and emotional hurdles during their recovery journey. Managing stress and prioritizing mental health are crucial aspects of their overall well-being. Let’s explore some key strategies to help support injured workers in navigating this often-overlooked aspect of their recovery process.
Acknowledging the Emotional Impact & Open Communication
 Sustaining an injury can be a traumatic experience, leaving injured workers feeling vulnerable and anxious about their future. Employers, colleagues, and support networks should validate these emotions and create an environment where workers feel comfortable expressing their feelings without judgment. Encourage open communication between the injured worker and their supervisors or case managers. Regular check-ins and updates can help alleviate stress and allow for adjustments to the recovery plan based on the worker’s needs.
Sustaining an injury can be a traumatic experience, leaving injured workers feeling vulnerable and anxious about their future. Employers, colleagues, and support networks should validate these emotions and create an environment where workers feel comfortable expressing their feelings without judgment. Encourage open communication between the injured worker and their supervisors or case managers. Regular check-ins and updates can help alleviate stress and allow for adjustments to the recovery plan based on the worker’s needs.
Provide Mental Health Resources, Encourage Selfcare and Work- Life Balance
Employers and case managers should ensure that mental health resources are readily available to injured workers. Access to counseling services, support groups, or Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) can be beneficial in managing stress and emotional challenges. Recovery can be physically and emotionally draining, making self-care essential. Encourage injured workers to take time for activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies they enjoy. Strive to maintain a healthy work-life balance during the recovery phase. Providing flexibility in work hours or offering remote work options (if possible) can help reduce stress and create a sense of control for the injured worker.
Monitoring Workloads, Responsibilities & Fostering a Supportive Work Environment
 Adjust workloads and responsibilities to accommodate the injured worker’s abilities during their recovery. Overloading them with tasks can exacerbate stress and hinder their healing process. During the recovery process, it’s essential to set realistic expectations for both the worker and the employer. Recovery may take longer than initially anticipated, and workers may experience setbacks. It is vital to provide ongoing support and understanding throughout this time. A positive and supportive work environment is crucial for an injured worker’s mental health. Colleagues can play a significant role in providing emotional support and encouragement during the recovery process.
Adjust workloads and responsibilities to accommodate the injured worker’s abilities during their recovery. Overloading them with tasks can exacerbate stress and hinder their healing process. During the recovery process, it’s essential to set realistic expectations for both the worker and the employer. Recovery may take longer than initially anticipated, and workers may experience setbacks. It is vital to provide ongoing support and understanding throughout this time. A positive and supportive work environment is crucial for an injured worker’s mental health. Colleagues can play a significant role in providing emotional support and encouragement during the recovery process.
Review and Revise the Recovery Plan
 Regularly review and revise the recovery plan with input from the injured worker. Flexibility is essential, as the recovery process can evolve over time. Managing stress and prioritizing mental health is critical for an injured worker’s recovery journey. Employers, colleagues, and support networks must work together to create a compassionate and understanding environment. By acknowledging the emotional impact of injuries, fostering open communication, providing mental health resources, and promoting self-care and work-life balance, we can support injured workers effectively throughout their recovery process. Together, let’s prioritize mental health and well-being as an integral part of the journey towards healing and returning to a fulfilling work life.
Regularly review and revise the recovery plan with input from the injured worker. Flexibility is essential, as the recovery process can evolve over time. Managing stress and prioritizing mental health is critical for an injured worker’s recovery journey. Employers, colleagues, and support networks must work together to create a compassionate and understanding environment. By acknowledging the emotional impact of injuries, fostering open communication, providing mental health resources, and promoting self-care and work-life balance, we can support injured workers effectively throughout their recovery process. Together, let’s prioritize mental health and well-being as an integral part of the journey towards healing and returning to a fulfilling work life.
Worker’s compensation cases can be complex and challenging for both employers and injured workers. Timely intervention is crucial to ensure that injured employees receive the necessary care and support, leading to better outcomes and reduced costs for employers. In this article, we will explore the numerous benefits of early intervention in worker’s compensation cases and how it can positively impact injured workers, employers, and the overall case management process. This article highlights the top six benefits of early intervention.
Faster Access to Medical Care:
 Early intervention in worker’s compensation cases enables injured workers to receive prompt medical attention, which is essential for a swift recovery. When injuries are addressed early, medical professionals can assess the severity of the condition and recommend appropriate treatment promptly. This not only minimizes the risk of complications but also facilitates a quicker return to work for the injured employee.
Early intervention in worker’s compensation cases enables injured workers to receive prompt medical attention, which is essential for a swift recovery. When injuries are addressed early, medical professionals can assess the severity of the condition and recommend appropriate treatment promptly. This not only minimizes the risk of complications but also facilitates a quicker return to work for the injured employee.
Reduced Recovery Time and Costs:
Early intervention can significantly reduce the recovery time for injured workers. Timely medical treatment and rehabilitation allow employees to heal more efficiently, preventing the development of chronic conditions or disabilities that may prolong their absence from work. Moreover, by addressing injuries early, employers can reduce the overall costs associated with worker’s compensation claims. Prompt treatment can prevent the need for extensive medical procedures or extended disability leaves, leading to substantial cost savings for employers and insurance providers.
Prevention of Secondary Injuries:
 Addressing injuries early can prevent the development of secondary injuries or complications. Some injuries, if left untreated, can lead to further health issues and prolonged recovery times. Early intervention allows medical professionals to identify and address potential risk factors, minimizing the chances of additional injuries or exacerbation of existing conditions.
Addressing injuries early can prevent the development of secondary injuries or complications. Some injuries, if left untreated, can lead to further health issues and prolonged recovery times. Early intervention allows medical professionals to identify and address potential risk factors, minimizing the chances of additional injuries or exacerbation of existing conditions.
Enhanced Case Management:
Early intervention enables case managers to engage with injured workers from the outset of the claim, building trust and rapport. This proactive approach fosters better communication and a deeper understanding of the injured employee’s needs and concerns. Additionally, early engagement allows case managers to stay ahead of potential challenges, such as identifying potential red flags for fraud or addressing any barriers to recovery promptly. A proactive approach to case management enhances the overall efficiency of the worker’s compensation process and helps ensure positive outcomes for all parties involved.
Positive Impact on Organizational Culture:
 Organizations that prioritize early intervention in worker’s compensation cases often cultivate a culture of care and support. When employees witness the employer’s dedication to their well-being, they feel valued and more inclined to invest their best efforts into the organization. Such a positive organizational culture can attract top talent and improve the employer’s reputation both internally and externally. It also sends a message that safety and well- being are paramount, encouraging employees to proactively report injuries and prioritize their health. Early intervention is a game-changer in worker’s compensation cases, benefiting both injured workers and employers. By addressing injuries promptly, employees gain faster access to medical care, reducing recovery time and costs. Employers, in turn, experience increased productivity and improved employee retention. Early intervention also leads to smoother claims processing, better return-to-work programs, and enhanced case management. Moreover, organizations that prioritize the well-being of their employees foster a positive culture and a more engaged workforce. Employers should establish clear protocols for reporting injuries and collaborate with case managers and medical professionals to ensure timely and comprehensive care for injured workers. By placing emphasis on early intervention, organizations can create a safer, healthier, and more productive work environment for all.
Organizations that prioritize early intervention in worker’s compensation cases often cultivate a culture of care and support. When employees witness the employer’s dedication to their well-being, they feel valued and more inclined to invest their best efforts into the organization. Such a positive organizational culture can attract top talent and improve the employer’s reputation both internally and externally. It also sends a message that safety and well- being are paramount, encouraging employees to proactively report injuries and prioritize their health. Early intervention is a game-changer in worker’s compensation cases, benefiting both injured workers and employers. By addressing injuries promptly, employees gain faster access to medical care, reducing recovery time and costs. Employers, in turn, experience increased productivity and improved employee retention. Early intervention also leads to smoother claims processing, better return-to-work programs, and enhanced case management. Moreover, organizations that prioritize the well-being of their employees foster a positive culture and a more engaged workforce. Employers should establish clear protocols for reporting injuries and collaborate with case managers and medical professionals to ensure timely and comprehensive care for injured workers. By placing emphasis on early intervention, organizations can create a safer, healthier, and more productive work environment for all.
A variety of injectable therapies is available to help workers’ compensations patients recover from musculoskeletal injuries. These therapies provide a range of benefits and applications for reducing inflammation, promoting tissue healing and regeneration, and are used in worker’s compensation cases for treating work-related injuries, as indicated. Here we review several types of injectable therapies and guidelines for their use.
Corticosteroids
The American College of Rheumatology supports the use of corticosteroid injections for the management of osteoarthritis for reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and improving function in the short-term. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can cause loss of cartilage and is generally not recommended.
 A retrospective study that included 91 patients with low back pain due to lumbar disc herniation found that transforaminal epidural corticosteroid injections prevented the need for surgery in 51 patients. However, workers’ compensations status had a significant effect on outcomes, with these patients receiving less benefit from the injections.
A retrospective study that included 91 patients with low back pain due to lumbar disc herniation found that transforaminal epidural corticosteroid injections prevented the need for surgery in 51 patients. However, workers’ compensations status had a significant effect on outcomes, with these patients receiving less benefit from the injections.
A 2018 study on cost-effectiveness of lumbar epidural steroid injections found that the therapy provided quality of life improvement in 45% of patients. Researchers concluded that the therapy may not be cost-effective for patients with lumbar degenerative disorders and further studies are needed to determine which patients will benefit. For cervical epidural steroid injections, a 3-month study found that the therapy provides significant quality of life improvement and is more cost-effective than conservative management in the short-term.
Hyaluronic Acid
A substance naturally present in the body, hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrates joints and connective tissues by attracting and holding onto water. HA injections are used to reduce inflammation and restore function to injured joints. There is supportive evidence for the use of HA in long-term pain relief and improvement in function for some musculoskeletal conditions, notably knee osteoarthritis. HA is the second-most common procedure for knee osteoarthritis after imaging and the most common treatment-specific procedure.
 HA vs. Platelet-Rich Plasma
HA vs. Platelet-Rich PlasmaIn a study that compared the cost-effectiveness of HA to platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy for knee osteoarthritis, HA injections yielded a cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) of $5,331 while PRP injections yielded a QALY of $8,635 over 12-26 weeks. However, after 1 year, PRP showed a significant advantage over HA, with a cost-effectiveness ratio of $12,628 per QALY.
HA injections were found to have a lower overall risk for adverse effects compared to oral NSAIDs, in a 2020 study, though risk of serious adverse effects (AEs) was similar. HA injections resulted in statistically significant but not clinically important improvement in knee pain and function compared to oral NSAIDs.
Platelet-Rich Plasma
Platelets release a variety of growth factors and immune-modulating cytokines that are helpful for healing soft tissue injuries. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a concentrated source of platelets that is used to speed tendon and cartilage healing and regeneration and reduce joint inflammation. A review of published studies compared PRP to HA for knee osteoarthritis PRP and determined that PRP was more effective for relieving pain and improving function within one year of treatment with no difference in risk of AEs. PRP has also been found to provide long-term improvement in knee osteoarthritis and tendinopathies.
Prolotherapy
 Prolotherapy is an injectable therapy that uses an irritant to stimulate the healing process. Prolotherapy is mainly used for regenerating injured soft tissues in chronic musculoskeletal pain conditions. A variety of irritant substances have been used in prolotherapy, including manganese, zinc, human growth hormone, ozone, glycerin, dextrose, and others. It has been found to provide long-term improvement in knee osteoarthritis and tendinopathies. A meta-review of prolotherapy using dextrose found it to be more effective than exercise one month after treatment and with similar efficacy to corticosteroids for chronic musculoskeletal pain of six months to one year duration.
Prolotherapy is an injectable therapy that uses an irritant to stimulate the healing process. Prolotherapy is mainly used for regenerating injured soft tissues in chronic musculoskeletal pain conditions. A variety of irritant substances have been used in prolotherapy, including manganese, zinc, human growth hormone, ozone, glycerin, dextrose, and others. It has been found to provide long-term improvement in knee osteoarthritis and tendinopathies. A meta-review of prolotherapy using dextrose found it to be more effective than exercise one month after treatment and with similar efficacy to corticosteroids for chronic musculoskeletal pain of six months to one year duration.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are used to promote the repair and regeneration of injured tissue. MSCs are capable of differentiating into multiple different mature cell types, as needed. They engage in a type of cell-to-cell signaling method called paracrine signaling, which makes them able to modulate the environment around them to promote healing, prevent scar tissue formation, inhibit inflammation, and promote collagen formation. MSCs are also easy to cultivate, making them cost-effective, and have low immune reactivity, which reduces the likelihood of adverse effects.
A meta-analysis that included 10 studies and 335 patients concluded that MSC therapy is safe and effective for knee osteoarthritis and resulted in a significant increase in cartilage volume.
Trigger Point Injections
 Both local anesthetic and botulinum toxin have been used as injectable therapies for myofascial trigger points, with the goal of reducing chronic muscle spasticity, dystonia (movement disorders), and myofascial pain. Local anesthetic has been found to be the more effective of the two. In a review of five published studies, four concluded that trigger point injections with botulinum toxin were ineffective for relieving pain. However, some studies report improvements in pressure/pain threshold with botulinum toxin therapy and botulinum toxin injections have been found to improve depression and anxiety scores. Trigger point injections can also be used to facilitate active therapies and assist with stretching affected muscles and joints.
Both local anesthetic and botulinum toxin have been used as injectable therapies for myofascial trigger points, with the goal of reducing chronic muscle spasticity, dystonia (movement disorders), and myofascial pain. Local anesthetic has been found to be the more effective of the two. In a review of five published studies, four concluded that trigger point injections with botulinum toxin were ineffective for relieving pain. However, some studies report improvements in pressure/pain threshold with botulinum toxin therapy and botulinum toxin injections have been found to improve depression and anxiety scores. Trigger point injections can also be used to facilitate active therapies and assist with stretching affected muscles and joints.
Use of Injectable Therapies for Spinal Injuries
 Spinal injection therapies have a higher risk profile compared to applications outside of the central nervous system. General complications may include temporary sensory and motor nerve block (neuropraxia), nerve injury (temporary or permanent), infection, headache, dizziness, as well as epidural hematoma, dural perforation, leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, or spinal meningeal abscess. Serious complications of spinal injections are rare but may include spinal cord damage, quadriplegia, ataxia, and death. Steroid injections may suppress the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis for up to three months.
Spinal injection therapies have a higher risk profile compared to applications outside of the central nervous system. General complications may include temporary sensory and motor nerve block (neuropraxia), nerve injury (temporary or permanent), infection, headache, dizziness, as well as epidural hematoma, dural perforation, leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, or spinal meningeal abscess. Serious complications of spinal injections are rare but may include spinal cord damage, quadriplegia, ataxia, and death. Steroid injections may suppress the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis for up to three months.
For cervical and lumbar injectable therapies, New York State workers’ compensation guidelines stipulate the following:
 Many individuals that have had to undergo an amputation as a result of a work accident may benefit from behavioral modules or therapies. These therapies can be adjusted to fit the needs of the individual, as well as may include the incorporation of a prosthetic. While physically attached to the body, prosthetics may be beneficial at also helping to alleviate associated emotional distress. The patient’s care providers should assist in guiding the patient if they are having difficulty coping at any stage in their healing process.
Many individuals that have had to undergo an amputation as a result of a work accident may benefit from behavioral modules or therapies. These therapies can be adjusted to fit the needs of the individual, as well as may include the incorporation of a prosthetic. While physically attached to the body, prosthetics may be beneficial at also helping to alleviate associated emotional distress. The patient’s care providers should assist in guiding the patient if they are having difficulty coping at any stage in their healing process.
 Prosthetist
Prosthetist This therapist will design and help execute an exercise regime for the injured worker with the goal of assisting them in regaining balance, coordination, and strength along with the new use of their prosthetic.
This therapist will design and help execute an exercise regime for the injured worker with the goal of assisting them in regaining balance, coordination, and strength along with the new use of their prosthetic.